Incremental Garbage Collection
Be aware
As of 5.4, it is and experimental feature. I advise to learn about it and try it, but remember that this feature is not production ready.
Problem
There is one major issue with Garbage Collector which Unreal Engine uses to manage memory occupied by UObject.
Garbage Collection runs every X seconds. But before memory can be “collected”, GC should decide which objects are considered “garbage”.
It is called reachability analysis. The main idea is to check references and mark unreachable objects for cleaning.
Yet when you have a lot of objects loaded, this process may take a while, leading to lags or stutters.
There are few ways to avoid this problem: disabling Garbage Collection during complex gameplay, pooling objects, etc.
Incremental Reachability Analysis
5.4 introduces new technique. Now we can split reachability analysis across multiple frames instead of running analysis in a single frame.
First of all, it doesn’t work with UPROPERTY and raw pointers. For incremental reachability analysis, TObjectPtr are required. (if you don’t know what this is, read here)
As soon as you mark TObjectPtr as UPROPERTY, it becomes trackable by engine.
Unreal’s source code is almost fully compatible with TObjectPtr, so you should prefer them to raw pointers.
Secondly, to enable IGC, add the following to your DefaultEngine.ini:
[ConsoleVariables]
gc.AllowIncrementalReachability=1 ; enables Incremental Reachability Analysis
gc.AllowIncrementalGather=1 ; enables Incremental Gather Unreachable Objects
gc.IncrementalReachabilityTimeLimit=0.002 ; sets the soft time limit to 2ms;
Performance
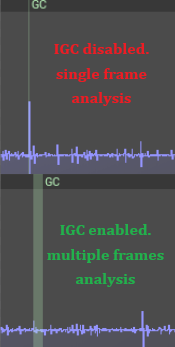
On this screenshot from Unreal Insight, we see how analysis is split across few frames, and there is no spike.
That’s how we can avoid hitches with incremental garbage collection.